📕 A Must Read Guide On Tokenomics
How to assess a token’s growth potential
Welcome to another free edition of Altcoin Investing Picks.
I hope you enjoyed our last issue “How much can you make in a bull market?”
In today’s post, I want to share a Must Read Guide on Tokenomics to help you invest in altcoins with more confidence.
Understanding tokenomics is one of the most important skills in crypto.
At its core, tokenomics, gives you a clear idea about a given token's supply and demand, allowing you to assess the token’s growth potential.
If you don't understand the tokenomics, all purchases are simply hoping that the price will move in the desired direction.
Let’s dive in!
1. The Basics
Token + Economics = Tokenomics
Just because a project looks valuable, doesn’t mean that this value gets transferred to you as a token holder.
Tokenomics is everything that impacts a token’s value - token creation and distribution, token burn schedules, and incentive mechanisms.
These factors come into two categories: Supply and Demand.
You can have a great project, but it can still be a bad investment if its token has bad tokenomics.
On the other side, it's still possible for a project to do well despite bad tokenomics such as meme coins. Sometimes the hype and pumpmentals are THAT strong.
P.S. See the Section #6: How to use Tokenomics below for more details.
2. Supply Metrics
Here are the two supply metrics you need to know:
Circulating Supply
What: tokens that are currently in circulation
How to use it: compare the circulating supply to the total supply to understand inflation potential. A high circulating supply relative to the total supply means fewer tokens are left to be mined or released.
Valuation: Market Cap (MC) → the total value in $ of circulating supply
Max Supply
What: total tokens that can exist
How to use it: a lower total supply can indicate scarcity, which might drive up demand and price if the token becomes popular.
Valuation: Fully Diluted Market Cap (FD or FDV)→ the total value in $ of total supply
How to find a token’s supply
Go to CoinGecko
Use the search bar at the top
Enter the crypto project
3. Why does supply matter?
When the maximum supply is reached, there will be fewer tokens available on the market. This makes the tokens more scarce. This affects a token’s price.
Generally,
Low supply → price appreciation
High supply → price depreciation
So, there are two paths a token can take:
Inflationary
Deflationary
The Inflation Rate is the rate at which new tokens are created and introduced into circulation.
A high inflation rate can dilute the value of existing tokens, whereas a low or fixed supply can create scarcity and potentially increase value.
Inflationary token
The token's supply can increase, and this is called emissions.
Emission is not good cause it usually leads to a decrease in value.
However, if the emission rate is slow and the total supply is still far away, it does not significantly impact the value.
Deflationary token
It can also happen that the token supply decreases over time.
This occurs when a project buys back tokens and burns them.
In theory, reducing the supply should increase the value.
4. Token Allocation & Distribution
The main factors that determine the launch and life of a token are its allocation and distribution.
Let’s discuss the key terminology to understand a token’s allocation and distribution:
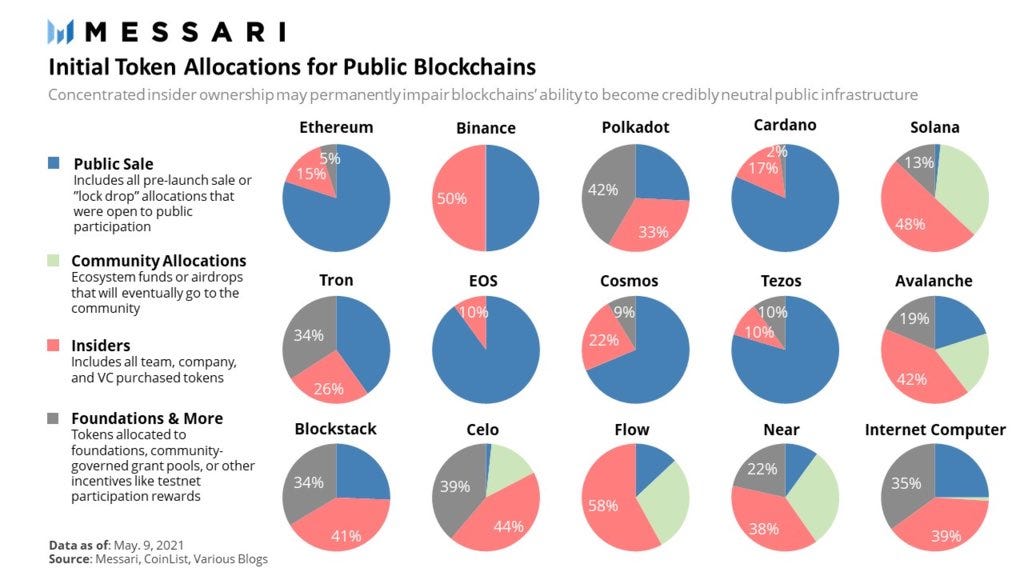
The Initial Distribution indicates how tokens are distributed at the initial offering, including allocation to founders, investors, and the community. Ensure the distribution is fair and not overly concentrated in the hands of a few. High centralization can lead to market manipulation.
Vesting Periods are timeframes during which certain tokens are locked and cannot be sold. They can prevent large dumps by early investors and founders, thus stabilizing the token price.
The day of the token launch is called TGE (Token Generation Event). TGE allocation is the percentage of tokens allocated to private sales (investors and key opinion leaders or KOLs), public sales (retail investors), marketing, ecosystem (staking, rewards, etc.), and airdrops.
Cliff is the period after TGE and before the next vesting.
Further resources:
5. Demand Side
The other side of the coin for the success of any token is demand.
In other words, the practical applications of the token within its ecosystem → what motivates people to buy that particular token.
For example, the dollar ($), despite significant inflation, has a huge demand cause people need it to pay their bills and live.
So, demand has an important relationship with supply because together they determine a token’s price within the market.
Generally,
Low demand → price depreciation
High demand → price appreciation
In general, 4 things drive demand for tokens:
Store of value → Bitcoin
Community/Speculation→ Memecoins
Utility → Smart Contract Platforms
Value Accrual → Staking Protocols
6. How to use Tokenomics
As we saw in the first section, good tokenomics does not always correspond to good market performance.
However, there are three core principles that we can use to leverage tokenomics analysis to invest better:
Tokenomics analysis is useful for long-term investments (e.g. Smart Contract Platforms, Micro Altcoins)
It makes no sense to use it for speculative operations (e.g. Tactical Portfolios, Narrative Trading)
It can’t be the only factor of analysis but must be combined with other elements (e.g. Market Potential, Market Valuation, Market Cycle, Community, Team, Backers, Narrative, Sector, etc.)
Take action 🚀
If you want to level up your crypto journey, consider subscribing to the premium package.
Here are some of our most popular premium posts:
By upgrading to Premium, you get the following:
Three articles per week (Tuesdays, Thursdays & Saturdays)
Full access to our entire library of analysis, picks & portfolios.
Access to the micro altcoin watchlist
Deep dive on micro altcoins with 10x+ potential
Hope to see you on the inside!
Cheers